If you hear a rear suspension noise such as clunking, grinding, or creaking, especially when moving over bumps, chances are there's a metal rubbing against another metal or car part. Several reasons can cause the rear suspension noise. In this article, we'll look at some of those reasons, locating and fixing the issues. But first, let's look at the function of the suspension system.
Rear suspension problems highlights
- Level of importance:medium
- Common reasons:road potholes, speed bumps, accidents, normal wear
- DIY inspection:possible but very complicated
- DIY repair:usually,impossible
- Average price in shops:$250 - $800
- Average time:3 - 6 hours
- If ignored:fatal failure, no drive, expensive repairs
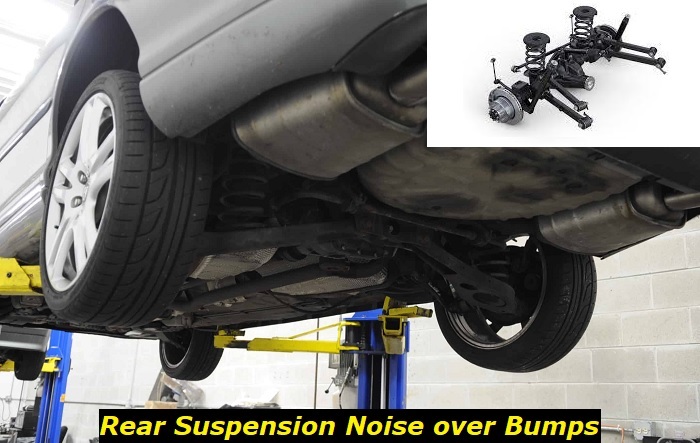

What is the Rear Suspension System
As the front suspension system handles the steering stability and traction of the car, the rear suspension prevents the vehicle's body from drooping and hitting the ground. The rear suspension system is divided into dependent and independent systems. The dependent system comes into play when the axle movement binds the wheel direction.
On the other hand, the independent system has the front and back wheels moving independently of the rear and front axle. The dependent rear suspension system is divided into two types: beam axle, which you can find in front-wheel drive cars, and solid axle, which you can find in rear-wheel drive cars.
The independent rear suspension is also divided into trailing arms suspension, which enables the rear wheels to move independently, and the short arm/long arm suspension, which consists of two lower control arms and two upper control arms. Whenever there is a noise from the rear suspension when the car moves over a bump, it signals an issue with the suspension system.
Causes of Rear Suspension Noise Over Bumps
You'll likely hear noise from the rear suspension when driving over bumps for various reasons. Some of the causes of the rear suspension noise are:
1) Worn Out Struts
Struts are part of the structural components found in the suspension system. They are almost similar to shock absorbers, except they are stronger because they are weight-bearing components.
Another difference to shocks is that they are mounted horizontally and appear as wheel extensions instead of ones mounted vertically behind the car tires. Bad struts that are worn out make a hollow metal-to-metal banging or clunking noise whenever the car moves over a bump or takes a corner.
To check the integrity of your struts or shocks, you can perform a bounce test where you push down the car at one corner and let go. The struts or shock are in good condition if the car bounces up and settles into its normal position. But if it bounces more than twice, the parts need replacing.
2) Damaged Shock Absorbers
Like the struts, shock absorbers may also get damaged due to wear and tear. A vehicle can have shocks or struts depending on its design. Shock absorbers look like springs, and their work is to provide comfort to passengers by absorbing the jolts caused by a rough terrain with rocks and bumps.
They also offer stability allowing you better steering control of your car. A damaged shock absorber makes a squeaking, clunking, or knocking sound when it bottoms out after hitting a pothole or a bump. It can also make a noise when taking a sharp turn. Apart from damaged shocks making the noise, unseated or not well-anchored shocks can also make a clunking noise.
3) Faulty Ball Joints
Ball joints are flexible ball and socket components of the suspension that provide a pivoting movement between the steering knuckles and the control arm. It has a similar function to the hip joint in the human body. If impurities such as dirt or grit enter the ball joint or the grease in the joints dwindles, the ball joints produce a faint intermittent rattling noise.
Excessive clearance in a joint because of wear and a loose joint can also cause noise. The noise usually escalates whenever the car passes through a dip or a bump. You can also hear it when the vehicle goes around a corner. A faulty ball joint can also cause steering drifts and cause the wheels to fall off if the damage is severe.
4) Dried-out or Sunken Rubber Bushing
A rubber bushing( also known as suspension bushing or shock bushing) is an elastic component fixed between two rigid suspension parts to create a flexible interface that prevents erosion of the two parts. It also reduces the vibration and noises created by the parts by buffering the energy created by the moving parts.
A dried-out or sunken suspension bushing makes a clunking noise similar to two metals banging onto each other. It can also produce a squeaking noise accompanied by vibrations synonymous with an old bed frame. The noise usually turns louder once you accelerate, pass through bumpy terrain, or take a sharp turn.
5) Loose Body Mounts
A body mount connects the motor vehicle frame to the vehicle's body. It has about 10-12 connection points with rubber bushings that cushion the vehicle's body against noise and vibration.
Over time, the rubber bushings on the body mount split and crack due to prolonged compression, causing the body mount to break down. This results in a squeaking or rattling noise from the mount's rubber bushings while driving on bumpy roads. Other signs of a loose or worn-out body mount are fender gaps, misaligned doors, and the car leaning on one side.
6) Flawed Control Arms
A control arm is a triangular hinged link between the vehicle's frame and the steering knuckle. It's also known as the A-arm. The control arm's function is to stabilize the car by ensuring that the movement of the car wheels and chassis is in unison. Depending on the design, a vehicle can have one or two control arms on the rear or front suspension.
A control arm can get damaged at its frame, bushing, or ball joint. The damage can result from a powerful collision, rust, or flexing. If the control arm is worn out, you'll likely hear an unusual popping noise when the vehicle is in motion which turns into a squeaking sound when the vehicle accelerates, takes a turn, or moves over a bump.
7) Broken Sway Bar
A sway bar, also known as an anti-roll bar or stabilizer bar, resists the car's tendency to move from side to side when the car takes a turn. The sway bar also connects the suspension parts on either side of the vehicle.
A sway bar may deteriorate over time due to rust and lack of lubrication, causing it to break. The sound of a broken sway bar is a clunking or popping sound produced due to the broken sway bar link hitting other suspension parts. A loose steering wheel is a common symptom of a broken stabilizer bar.
8) A Bent or Damaged Axle Shaft
An axle shaft is a load-bearing car component that supports the car's weight and transfers the rotational force from the transmission system to the car wheels. The axle shaft can bend when the car drives over bumps, curbs, or hits a pothole at high speed.
If the axles become damaged, the car strains to move and may also make clunking or sputtering sounds because the car struggles to transfer the power from the transmission to the wheels. Continuing to drive a car with a damaged or bent axle can cause the axle to break, and it won't be able to move anymore.
9) Poor Lubrication of the Suspension system
The suspension parts, like the moving parts of other car systems, need lubrication to prevent wear and tear whenever there is metal-to-metal contact. It also helps the suspension parts to move easily. Proper lubrication allows a smooth driving experience. A common lubricant of the suspension system is grease.
If the suspension system lacks enough lubrication, you'll likely notice a loud squeaking from underneath the car when the car moves over bumps or goes through rough terrain.
How to Fix the Rear Suspension Noise
Some of the ways to fix the rear suspension noise are:
- Since you cannot rebuild struts, they need replacing. Some struts also have a replaceable cartridge if it becomes worn out. Most strut manufacturers recommend replacing the struts every 50000 miles. Replacing struts is dangerous and should only be left to the experts.
- You can repair a leaking shock absorber and replace a worn-out one to eliminate the rear suspension noise. The average lifespan of shock absorbers spans 4-8 years and mostly depends on the road conditions you drive on.
- A worn-out ball joint also needs replacing. To replace the ball joint, you'll need to remove the car wheel to access it. Using new bolts on the replaced ball joints is advisable to prevent corrosion.
- You can use a lithium-based or silicone-based lubricant to silence a squeaky dried-out rubber bushing.
- Replacing the body mount bushings or the body mount itself can also help eliminate the noise. To enable swapping the damaged body mount bushing with new ones, one needs to separate the body of the car from the frame.
- With control arms, you can repair or replace the control arms or control arm bushings. Repair parts or performance parts are available options when it comes to replacing or repairing the control arm. Repair parts are also known as original equipment manufacturers(OEM) since they have the same specifications. Conversely, performance parts have better specifications than the original manufacturer's parts.
- It would help if you replaced the sway bar links in pairs to prevent having a worn-out part on one side of the vehicle. While replacing, ensure you get high-quality, durable, and stiffer sway bar end links from a trusted brand. The sway bar design should also fit the year and model of your car.
- You don't have to replace a bent axle shaft, but you can seek the service of an alignment technician to align it for you. You'll have to replace an extremely bent or broken axle shaft.
- A lithium-based or silicone-based lubricant comes in handy to solve the problem of a squeaky rear suspension. A grease gun is useful when applying the lubricants over the suspension parts. Some suspension parts are not accessible without removing the car wheel.
Bottom Line
There you go-reasons for rear suspension noise over bumps and how to locate and fix the issues. If you cannot diagnose or fix the issue, you should visit a trusted auto shop for repair or replacement.
About the authors
The CarAraC research team is composed of seasoned auto mechanics and automotive industry professionals, including individuals with advanced degrees and certifications in their field. Our team members boast prestigious credentials, reflecting their extensive knowledge and skills. These qualifications include: IMI: Institute of the Motor Industry, ASE-Certified Master Automobile Technicians; Coventry University, Graduate of MA in Automotive Journalism; Politecnico di Torino, Italy, MS Automotive Engineering; Ss. Cyril and Methodius University in Skopje, Mechanical University in Skopje; TOC Automotive College; DHA Suffa University, Department of Mechanical Engineering





Add comment