We’ve looked at every Tesla EV modification that has ever been mass produced.
In our research, we looked at performance, driving range, energy consumption, and other Tesla statistics. We compared Tesla’s electric vehicles with other electric cars, as well as cars equipped with internal combustion engines.
In this article, we want to share what we’ve learned.
Here are our main findings on Tesla stats and figures:
- Over 13 years of production, Tesla has increased its engine power by an average of 23.4%.
- Tesla cars are 157.8% more powerful than cars with internal combustion engines.
- Tesla cars can go an average of 293 miles (471.1 km) without recharging.
- The average electricity consumption of Tesla EVs is 20.9 kWh per 60 miles.
- On average, Tesla has 67.7% more battery capacity than other EVs.
- The average maximum speed of Tesla electric cars is 12.3% higher than that of cars with internal combustion engines.
- 43% of Tesla models are SUVs.
- 59% of Tesla modifications are equipped with all-wheel drive.
- Tesla cars can accelerate 118.9% faster than ICE vehicles.
- Tesla makes cars that are 62.8% more powerful than other electric vehicles on the market.
Let’s have a more specific look at all key points.
Tesla has increased its engine power by an average of 23.4% over 13 years
Let’s start with Tesla statistics overtime. Since 2012, Tesla has released new models, new versions of existing models, or facelifts every year. The only year without a significant update was 2018.
Tesla’s lineup:
- Roadster – 2008
- Model S – 2012
- Model X – 2015
- Model 3 – 2017
- Model Y – 2020
- Cybertruck – 2021
- Roadster 2nd Gen – 2022
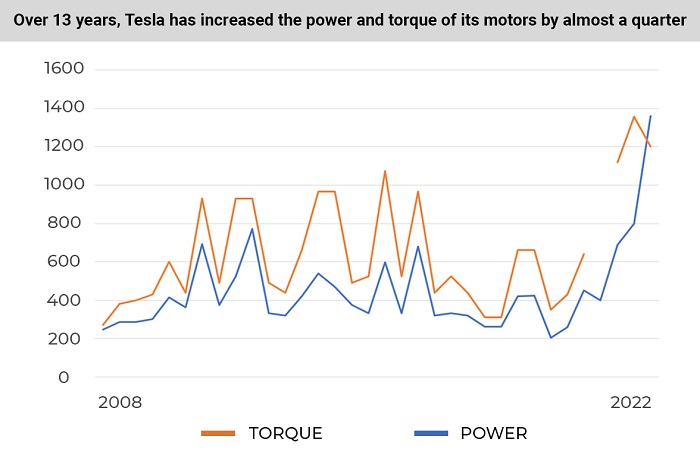
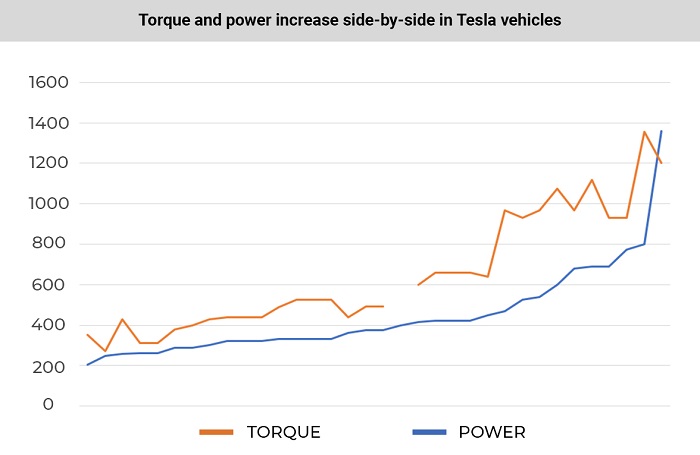
The average power of the first 10 modifications was 427 hp (314 kW). The average power of the latest 10 modifications is 527 hp (388 kW). Over the 13 years of its life, Tesla has, on average, increased the power of its motors by 100 hp (74 kW), or 23.4%.
The average torque of the first 10 modifications was 580 Nm. For the latest 10 modifications, it’s 703 Nm. The company has increased the average torque of its engines over 13 years by 123 Nm, or 21.2%.
Of the first 10 Tesla modifications, 6 had rear-wheel drive and 4 were equipped with all-wheel drive. Of the latest 10 modifications, 3 have rear-wheel drive and 7 use all-wheel drive. As the company has developed, it has begun to favor all-wheel-drive systems for its vehicles.
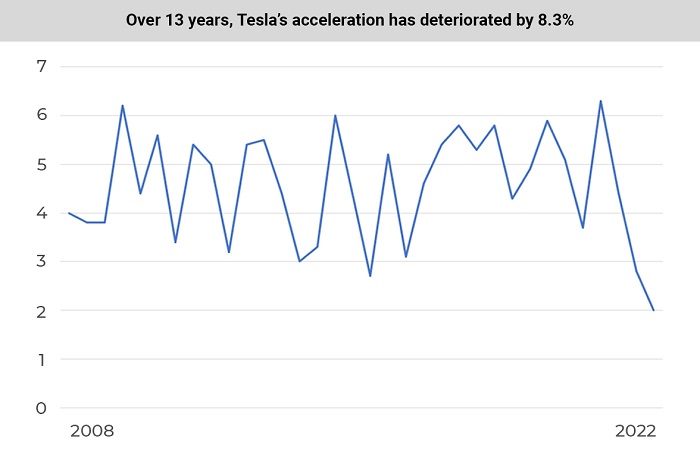
The first 10 Tesla modifications accelerated to 60 mph in an average of 4.28 seconds. For the latest 10 modifications, this indicator is 4.42 seconds. Over the past 13 years, Tesla cars have become 0.14 seconds slower at accelerating to 60 mph; that is, their dynamics became 3.3% worse.
The first 10 modifications showed an average top speed of 137 mph (220 km/h). For the latest 10 modifications, the indicator has been 146 mph (235.5 km/h). Tesla vehicles have added 9 mph (15.5 km/h) to their top speed and become 7% faster in the past 13 years.
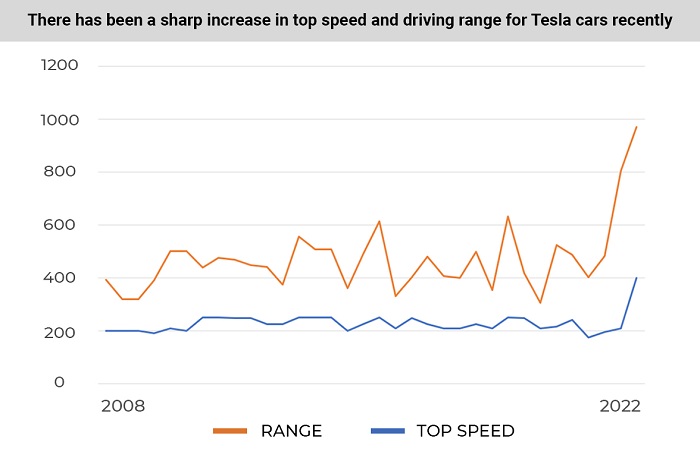
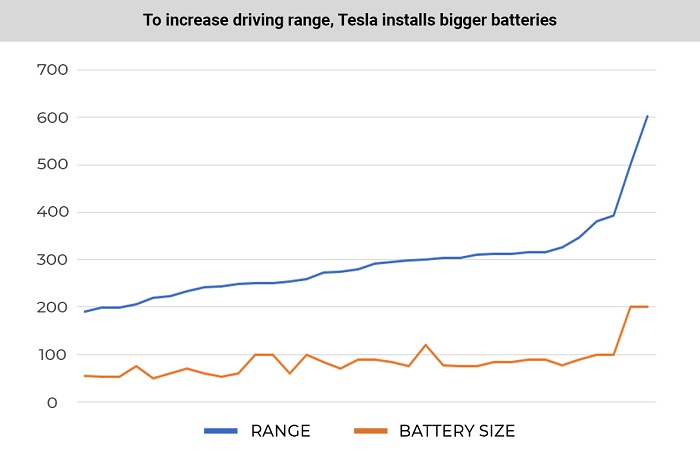
The first 10 Tesla modifications showed an average driving range of 264.7 miles (426 km). The latest 10 modifications show 334.3 miles (538 km). Tesla vehicles have added 69.6 miles (112 km) to their range over the past 13 years and improved their specification in this area by 26.3%.
The first 10 modifications had an average battery capacity of 73.9 kWh. The latest 10 modifications have a battery capacity of 108.1 kWh, on average. Tesla cars have added 34.2 kWh to their battery capacity, or 46.3%.
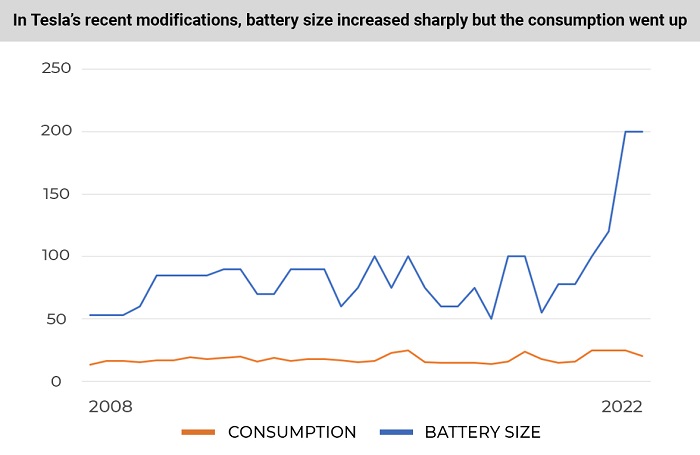
The first 10 modifications showed an average power consumption in optimal conditions of 16.6 kWh per 60 miles. For the latest 10 modifications, this figure is 19.2 kWh per 60 miles. Over the past 13 years, Tesla vehicles have increased electricity consumption by 2.6 kWh per 60 miles, or 15.7%.
Over the past 13 years, Tesla vehicles have become 23.4% more powerful and have added 21.2% of torque. The number of all-wheel-drive vehicles has increased. New Tesla stats says that the cars are 7% faster, and they can travel 26.3% further without recharging. Tesla also added 46.3% battery capacity to their cars. However, modern Tesla electric vehicles accelerate 3.3% more slowly and consume 15.1% more electricity than older Tesla cars.
Tesla cars are, on average, 157.8% more powerful than ICE cars
Comparison data for Tesla electric vehicles versus vehicles equipped with internal combustion engines (average calculated data shown):
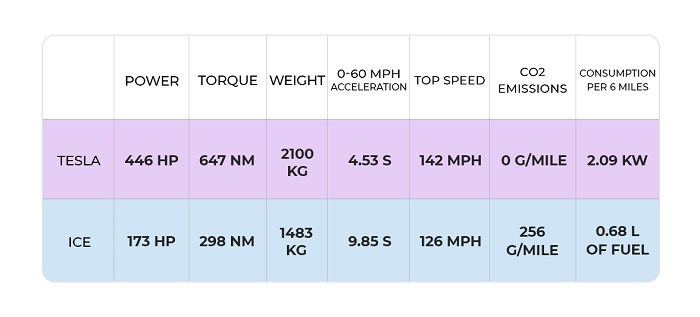
Tesla cars are 157.8% more powerful than ICE cars. Electric Tesla cars accelerate 118.9% faster than ICE cars.
In terms of fuel consumption, Tesla electric vehicles consume 3.1 kW of electricity, and cars with internal combustion engines use, on average, 1 liter of fuel over the same distance.
Tesla cars are apparently better in all areas than ICE cars. Tesla electric cars are more powerful, have more torque, and accelerate significantly faster.
On average, Tesla electric cars have a 293 mile (471.1 km) driving range
Tesla vehicles have a driving range of 190 to 603 miles (306 to 970 km). On average, Tesla EVs have a range of 293 miles (471.1 km).
Basic data on 10 cars with the longest range and 10 cars with the shortest range (among Tesla models):
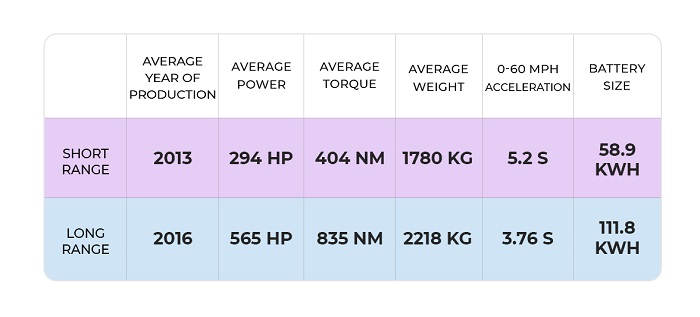
We found that in newer vehicles, Tesla’s specs are nearly twice as good, and there is a significant increase in battery size, which has made it possible not only to maintain but also to increase the range.
On average, Tesla electric vehicles consume 20.9 kWh per 60 miles
Time to turn to some hidden Tesla stats, not stated by the producer. The actual electricity consumption, according to our calculations, for Tesla electric vehicles ranges from 15.7 kWh per 60 miles to 28.9 kWh per 60 miles. The average electricity consumption for Tesla vehicles is 20.9 kWh per 60 miles.
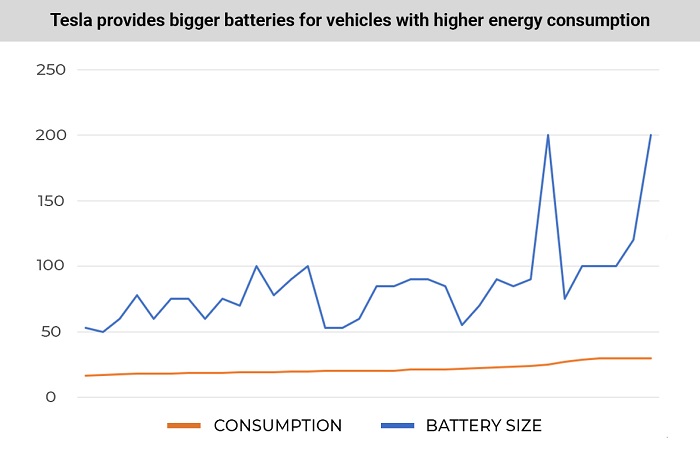
We analyzed the 10 most energy efficient and 10 least energy efficient Tesla vehicles to find out which factors influence consumption the most:
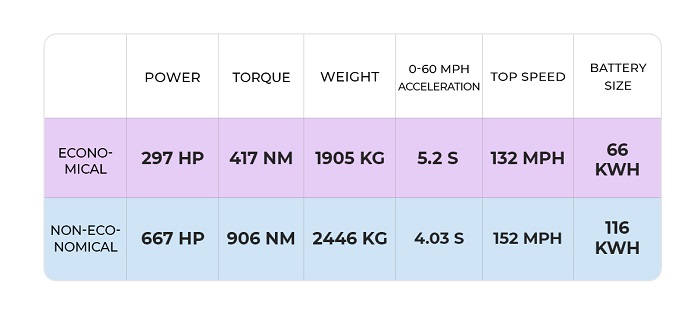
Obviously, an increase in engine power and torque increases the electricity consumption of Tesla vehicles. The weight of the car also affects the consumption indicator. To compensate for the high consumption in the Tesla premium series, much larger batteries have been installed.
Tesla batteries have, on average, 67.7% more capacity than other EVs
The Tesla battery size ranges from 50 to 200 kWh. The average capacity is 85.6 kWh.
On average, electric vehicles have a battery size of 51.03 kWh. Tesla vehicles offer 67.7% more battery capacity than other electric vehicles.
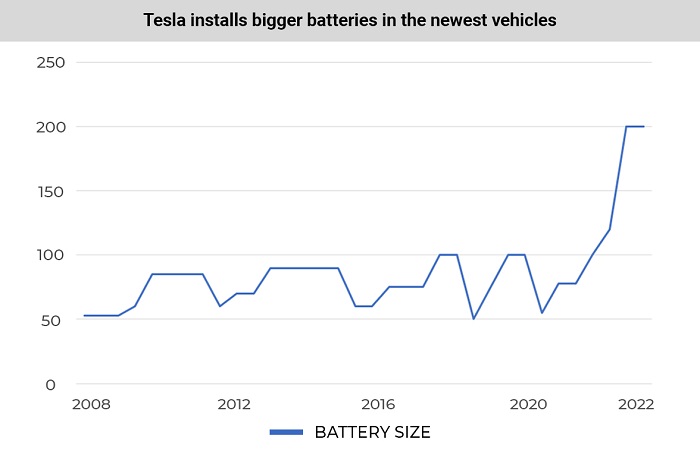
Statistics show that Tesla is gradually switching to larger batteries, which allows an increase in driving range while maintaining, and even improving, the cars’ specifications.
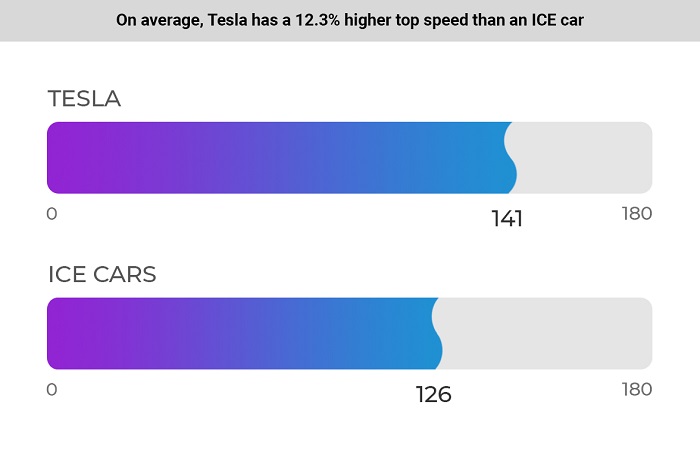
Tesla vehicles have 12.3% higher top speeds than ICE vehicles
Tesla vehicles have a top speed that is between 109 mph (Tesla Cybertruck Single Motor) and 249 mph (Tesla Roadster 2 Gen). The average maximum speed for all cars is 142 mph.
On average, cars with internal combustion engines have a maximum speed of 126 mph. Tesla cars can reach 12.7% faster speeds.
The top speed of Tesla’s electric vehicles is influenced by their power and torque specs. For the fastest cars, the power and torque are almost twice as high as those of the slowest modifications. Tesla also installs the biggest batteries in the most productive cars (in terms of maximum speed).
43% of Tesla cars are SUVs
Tesla has launched only 7 car models. The body types are as follows:
- SUV – 2
- Coupe – 1
- Liftback – 1
- Pickup – 1
- Roadster – 1
- Sedan, Fastback – 1
Given the focus of the Cybertruck pickup in the SUV segment, it can be assumed that 43% of Tesla vehicles are presented in the crossover and SUV segments.
59% of Tesla modifications are equipped with all-wheel drive
Tesla uses only two types of drive on its cars – rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive. There is no front-wheel-drive Tesla.
Of the 34 modifications of Tesla electric vehicles, 20 cars (59%) are equipped with all-wheel drive and 14 cars (41%) have rear-wheel drive.
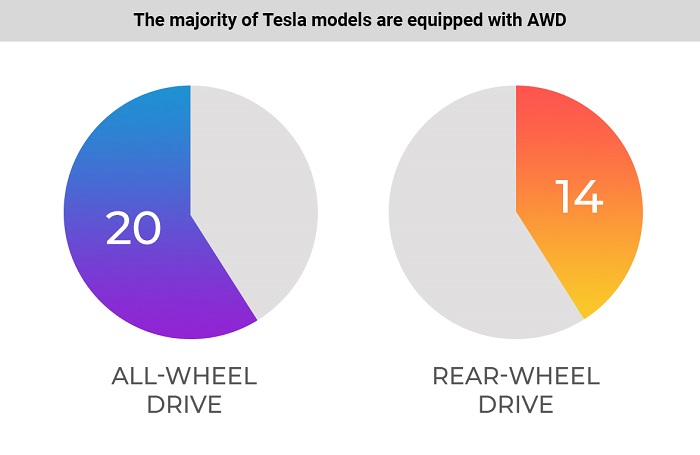
Tesla’s rear-wheel drive is older. The average year of production of rear-wheel-drive modifications is 2014. The average year of production of four-wheel-drive vehicles is 2016.
Of the 7 models, only the Roadster 1 Gen and Model 3 are not equipped with four-wheel drive in any modification.
Model Y and Model X crossovers do not have rear-wheel-drive modifications; they are sold only with AWD.
Tesla cars accelerate 118.9% faster than ICE cars, on average
The fastest car is the Tesla Roadster 2 Gen 2022 (1.9 s to 60 mph). The slowest is the Tesla Cybertruck Single Motor (6.5 s to 60 mph).
On average, Tesla cars accelerate to 60 mph in 4.35 seconds. The world’s average acceleration rate is 9.52 seconds to 60 mph. Tesla is 118.9% faster than the market average.
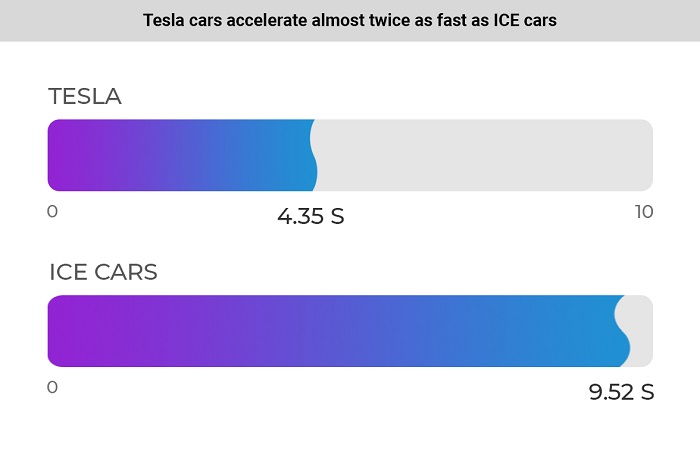
The sample showed that in the case of Tesla, a twofold increase in engine power leads to a nearly twofold improvement in acceleration performance. This shows the high efficiency of Tesla’s electric motors.
Tesla electric cars are 62.8% more powerful than other electric cars
Tesla cars have an average power of 446 hp (333 kW). Other EVs have an average power of 274 hp, making Tesla 62.8% more powerful than the EV market average.
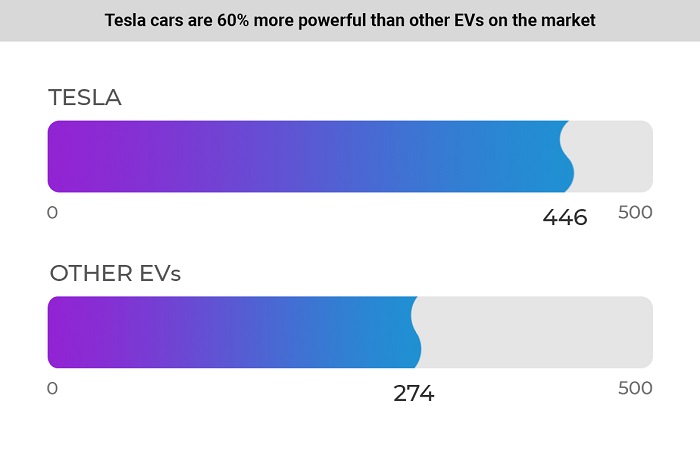
Tesla’s torque is 52.2% higher than that of other electric cars.
The most powerful car (the Tesla Roadster 2 Gen) is 567% more powerful than the weakest one (Tesla Model 3 2017) at 1360 hp and 204 hp respectively.

Tesla makes the most efficient electric vehicles on the market, vastly outperforming its competitors. At the same time, in the Tesla model range itself, there is more than a fivefold difference in power.
In this file you'll find the data we used for our research
Thank you for reading our Tesla statistics article. If you have any questions or want to add to the data in the study, please contact us in the comments section below.
About the authors
The CarAraC research team is composed of seasoned auto mechanics and automotive industry professionals, including individuals with advanced degrees and certifications in their field. Our team members boast prestigious credentials, reflecting their extensive knowledge and skills. These qualifications include: IMI: Institute of the Motor Industry, ASE-Certified Master Automobile Technicians; Coventry University, Graduate of MA in Automotive Journalism; Politecnico di Torino, Italy, MS Automotive Engineering; Ss. Cyril and Methodius University in Skopje, Mechanical University in Skopje; TOC Automotive College; DHA Suffa University, Department of Mechanical Engineering






Add comment